Relief valves
Relief valves are used as pressure-limiting devices to protect hydraulic systems and components. With flow ratings up to 380 l/min [100 US gal/min] and pressure ratings up to 400 bar [5,800 psi], our relief valves are available in various types, including direct acting, differential area, pilot operated, bi-directional, and crossover HIC.
Features and benefits
- Relief valves are commonly used for work port relief applications, shock protection, and load sense circuits as load sense pump relief, and can be used as pilot valves for logic elements.
- Direct-acting designs are available with damping for quiet, stable performance.
- Differential-area and direct-acting designs offer fast response and low leakage.
- Pilot-operated designs provide stable response and precise control across varying flow rates.
- Free-reverse-flow designs are available for improved circuit flexibility.
Applications
- Agriculture
- Construction
- Cranes and material handling
- Forestry
- Lawn and turn
- Road building
Basic operation
Relief valves are pressure limiting devices. They open when the inlet pressure exceeds the pressure setting of the valve, which is derived by pressure acting against a spring force. The point at which the valve begins to open is known as the crack pressure. The force created by the spring can be adjusted to achieve the required pressure setting. There are various types of relief valves available as shown below.
Direct-acting poppet type
A direct acting, poppet type relief valve blocks flow from port 1 to 2 until there is sufficient pressure to overcome the spring force and move the poppet off its seat, opening the valve. As the pressure increases, the poppet will be forced further back against the spring allowing more flow to tank. The valve will re-seat when the pressure falls below the pressure setting. These valves are ideal as system relief valves where the flow across the valve is intermittent and then constant.
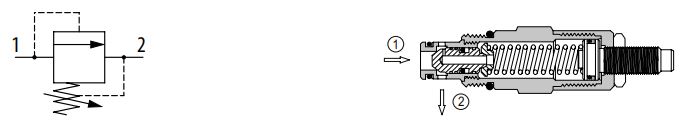
Direct-acting spool type
Similar in operation to the poppet type, a spool type design helps to remove instability and offers good control over varying flows at low pressure. These are ideal for use as a purge relief in a closed loop circuit.
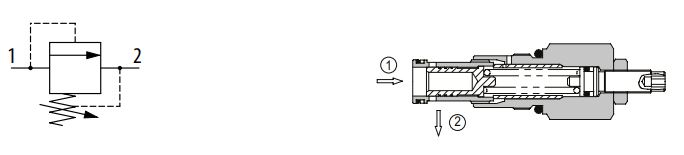
Differential area poppet type
A differential area, poppet type relief valve blocks flow from port 2 to 1 until there is sufficient pressure to open the valve. The pressure acts on the differential area between the seal on the outside diameter on the poppet and the seat diameter, overcoming the spring force to move the poppet off its seat and open the valve. These valves are very fast acting, making them ideal for use in clipping pressure spikes.
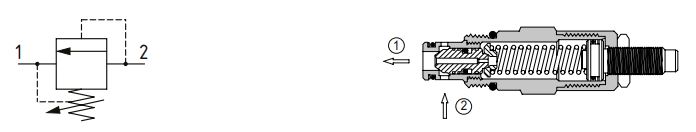
Bi-directional poppet type
A bi-directional, poppet type valve is a dual cross over relief valve in one cartridge. When the pressure exceeds the setting, the valve will open from port 1 to 2 or port 2 to 1 depending on where the pressure is applied. The pressure setting will be the same in both directions. These are ideal for use as cross over relief valves in motor applications.
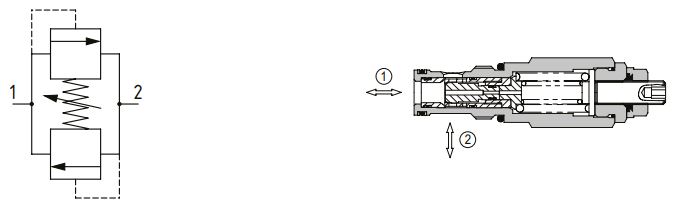
Pilot-operated spool type
A pilot operated, spool type relief valve blocks flow from port 1 to 2 until there is sufficient pressure to overcome the spring force and move the poppet off the pilot seat. This creates a pressure differential across the spool, causing the spool to overcome a lighter spring and open the valve. They are suited to be main system relief valves where precise pressure control is required.
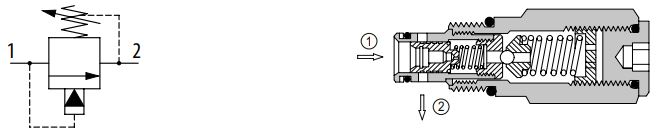
Ventable pilot-operated spool type
A ventable, pilot operated, spool type relief valve blocks flow from port 1 to 2 until there is sufficient pressure to overcome the spring force and move the poppet off the pilot seat. This creates a pressure differential across the spool, causing the spool to overcome a lighter spring and open the valve. The vent port allows the valve setting to be controlled remotely using a pilot relief valve or a pilot proportional valve.
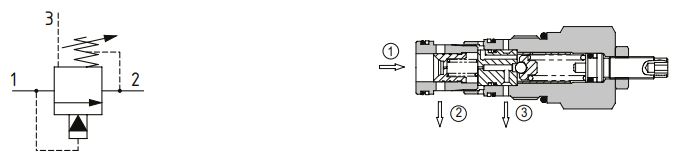
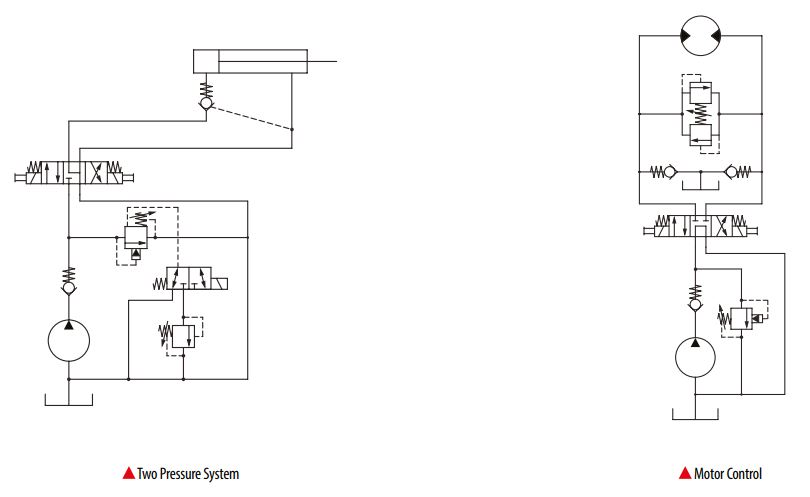
Typical application diagrams
Relief valve comparison
|
Characteristic/type
|
Direct -acting spool
|
Direct-acting poppet
|
Direct-acting damped poppet
|
Differential-area poppet
|
Pilot-operated spool
|
|
Leakage
|
-
|
+
|
+
|
+
|
-
|
|
Pressure rise
|
- |
-
|
-
|
+
|
+
|
|
Hysteresis
|
+
|
+
|
+
|
-
|
- |
|
Dirt tolerant
|
-
|
+
|
-
|
+
|
- |
|
Fast acting
|
- |
+
|
-
|
+
|
-
|
|
Stable
|
-
|
-
|
+
|
+
|
+
|
|
Relative price
[1 lowest]
|
4
|
2
|
3
|
1
|
5
|
|
Rule of thumb
|
Charge relief
|
Limiting Pressure
|
Regulating, low flow, quiet
|
Limiting and regulating pressure
|
Regulating pressure
|